This publication presents a novel approach aimed at improving biometric protection in Internet of Things (IoT) environments. The method focuses on producing cancelable biometric templates that prioritize both security and privacy. By utilizing Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) to break down biometric signals into fundamental components and encoding these using quaternion-based techniques, the system generates templates that cannot be reversed and are exceptionally resistant to spoofing attempts.
The approach delivers impressive performance, achieving an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.9997 and an Equal Error Rate approaching zero, all while maintaining low computational requirements. This makes the solution especially appropriate for IoT devices where processing capabilities are often limited. The findings highlight the method’s strong potential to tackle key security concerns in biometric applications within IoT networks.
This research exemplifies Sano’s dedication to developing secure, resource-efficient, and privacy-conscious technologies at the crossroads of biometrics, artificial intelligence, and computational neuroscience.
Authors: Mahmoud Nasr, Krzysztof Brzostowski, Adam Piórkowski, Fathi E. Abd El-Samie
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-89491-2
Keywords: Quaternion Mathematics, ComputationalSecurity, EMD, IoT
READ HERE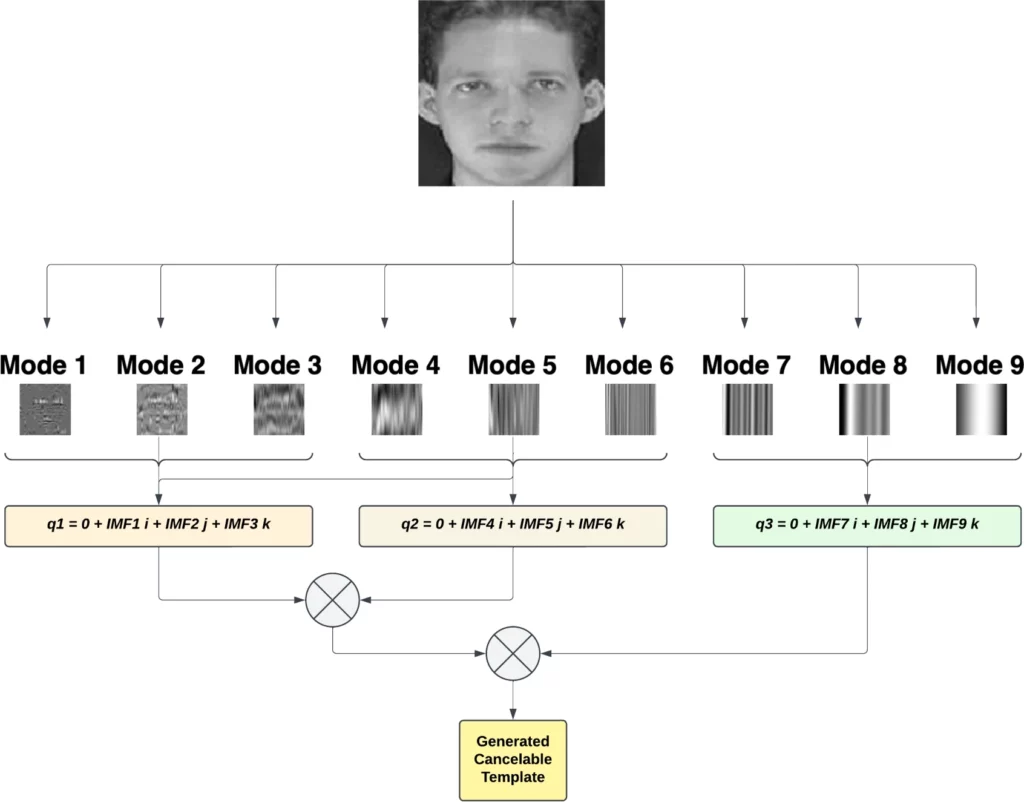
Image Source: www.nature.com/articles

